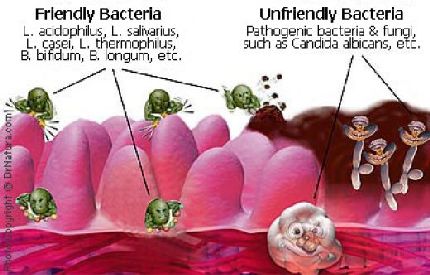
What is it? Resistance to antibiotics is a worldwide public health problem that continues to grow. This occurs when strains of bacteria in the body become resistant to antibiotics as a result of misuse and abuse of antibiotics. How many people it affects? Hospitals, 190 million doses of antibiotics administered daily. Among non-hospitalized patients, more than 133 million treatment courses of antibiotics prescribed annually doctors. It is believed that 50 percent of the latter prescriptions are not needed, so they prescribed for colds, coughs and other viral infections. The most frequent causes of many people, or expect or ask their doctors prescribe antibiotics when they feel sick or have a common cold. Patients should understand, however, that antibiotics designed to treat bacterial infections, not viral infections. And many times a cold is a viral infection. The only way to tell a cold or illness is bacterial infection, and whether it should be treated with antibiotics for a doctor to check it out. If you have a sore throat your doctor should be tested throat culture. If test results show that bacterial infection is present, then antibiotics should be prescribed to treat the infection. There is no sure way to know if a cold or disease is a bacterial infection without testing. Misuse and abuse of antibiotics has led to the development of resistance to antibiotics. The most common misuse and abuse of antibiotics are:
not complete the full dose of antibiotics. If an antibiotic prescription is not completed (even if you leave one or two tablets), it leaves some bacteria alive and "persistent" for future antibiotic treatment. How can this be prevented? And doctors and patients should play a strattera without prescritpion role in reducing the abuse of antibiotics. Antibiotics may be established only at test (eg, throat culture) shows that the bacterial infection is present. Antibiotics are not effective in combating viral infection. However, patients often require that their doctors prescribe antibiotics when they are not needed. Taking antibiotics when you have a viral infection not only spend time and money, but also enhances resistance to antibiotics. Patients should ask their doctor if they have a viral or bacterial infection and that tests were conducted to prove it. Doctors also have to change their practice assignment and only prescribe antibiotics for their patients if bacterial infection is present. Download this page containing the information on this page. Download of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under the title
Reserve Treasure: Know When Antibiotics Work. (Free reader required to view these brochures.)
Search resistance to antibiotics in the ACP. Annals of Internal Medicine is a leading peer-reviewed internal medicine clinical journal. .
No comments:
Post a Comment